The trend for Horn & Co. is positive, which could indicate better collections, faster inventory turnover, or that the company has been able to pay down debt. By contrast, in the case of Company Y, 75% of the current assets are made up of these two liquid resources. Advisory services provided by Carbon Collective Investment LLC (“Carbon Collective”), an SEC-registered investment adviser. For instance, a high working capital ratio for a company in the technology industry might be different from a high working capital ratio for a company in the retail industry. A ratio higher than 2.00 might indicate that a company has too much debt and is not as financially healthy as creditors would like.
- The current ratio is called current because, unlike some other liquidity ratios, it incorporates all current assets and current liabilities.
- The working capital ratio is slightly different, as it shows the relationship between assets and liabilities proportionally.
- On the other hand, the current liabilities are those that must be paid within the current year.
- A ratio higher than 2.00 might indicate that a company has too much debt and is not as financially healthy as creditors would like.
- Therefore, this compensation may impact how, where and in what order products appear within listing categories, except where prohibited by law for our mortgage, home equity and other home lending products.
To calculate the ratio, analysts compare a company’s current assets to its current liabilities. However, if the current ratio of a company is below 1, it shows that it has more current liabilities than current assets (i.e., negative working capital). This is because these assets are easily convertible to cash, unlike fixed assets. Acceptable current ratios vary by sector, but they should be between 1.5 percent and 3 percent for healthy organizations. If a company’s current ratio is in this range, it usually means it has strong short-term financial health.
Formula For Current Ratio
Conversely, a firm that may appear to be failing presently might be making solid progress toward a stronger current ratio. Suppose we’re evaluating the liquidity of a company with the following balance sheet data in Year 1. One shortcoming of the metric is that the cash balance includes the minimum cash amount required for working capital needs.
For example, a normal cycle for the company’s collections and payment processes may lead to a high current ratio as payments are received, but a low current ratio as those collections ebb. Calculating the current ratio at just one point in time could indicate that the company can’t cover all of its current debts, but it doesn’t necessarily mean that it won’t be able to when the payments are due. The first way to express the current ratio is to express it as a proportion (i.e., current liabilities to current assets). As a rule of thumb, if your company has a working capital ratio of less than 1, then this may indicate that you are facing liquidity problems.
Sustainable Investing Topics
Similarly, Walt Disney owned 81 cents in current assets for every dollar in current debt. Meanwhile, Apple has more than enough cash on hand to satisfy its present commitments if they were all due right away and its current assets could be converted to cash. A current ratio of equal to or slightly greater than the industry average is typically seen as appropriate. Conversely, a lower current ratio than the industry norm might imply a higher risk of default or trouble. Similarly, if a company’s current ratio is unusually high relative to its peers, it suggests that management isn’t making the best use of its assets. In comparison to the current ratio, the quick ratio is considered a more strict variation due to filtering out current assets that are not actually liquid — i.e. cannot be sold for cash immediately.
- To offer an example, a current ratio of 3 indicates that the company’s current assets exceed its current liabilities by 3 times.
- Conversely, a company with a negative working capital means the business lacks liquid assets to cover its current or short-term liabilities, usually due to poor asset management and cash flow.
- Similarly, Walt Disney owned 81 cents in current assets for every dollar in current debt.
- Large retailers can also minimize their inventory volume through an efficient supply chain, which makes their current assets shrink against current liabilities, resulting in a lower current ratio.
- Although the total value of current assets matches, Company B is in a more liquid, solvent position.
- In contrast, the current ratio also includes inventory, an asset that cannot be converted to cash in most situations within 90 days or less.
Over-trading companies are likely to face substantial difficulties in meeting their day-to-day obligations. GoCardless is a global payments solution that helps you automate payment collection, cutting down on the amount of financial admin your team needs to deal with. The On-Base Percentage is calculated by adding up all of the bases a player gets and dividing that by the number of at-bats they had…. Introduction Chat GPT OpenAI’s ChatGPT and GPT-3 and GPT-4 API are powerful language generation tools that can be used for a wide range of applications….
Current Ratio Formula – What are Current Liabilities?
Public companies don’t report their current ratio, though all the information needed to calculate the ratio is contained in the company’s financial statements. This is because it could mean that the company maintains an excessive cash balance or has over-invested in receivables and inventories. Generally, the assumption is made that the higher the current ratio, the better the creditors’ position due to the higher probability that debts will be paid when due. If your current ratio is low, you’ll have a hard time paying off your current obligations and liabilities.
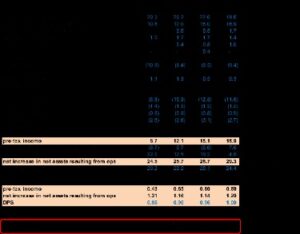
This would be worth more investigation because it is likely that the accounts payable will have to be paid before the entire balance of the notes-payable account. Company A also has fewer wages payable, which is the liability most likely to be paid in the short term. Finally, the operating cash flow ratio compares a company’s active cash flow from operating activities (CFO) to its current liabilities. This allows a company https://kelleysbookkeeping.com/gross-profit-vs-net-income/ to better gauge funding capabilities by omitting implications created by accounting entries. This means that Apple technically did not have enough current assets on hand to pay all of its short-term bills. Analysts may not be concerned due to Apple’s ability to churn through production, sell inventory, or secure short-term financing (with its $217 billion of non-current assets pledged as collateral, for instance).
On the other hand, a ratio higher than 1 shows the company is capable of paying all its liabilities, while still keeping some current assets. Because this ratio measures assets as a portion of Current Ratio Calculator Working Capital Ratio liabilities, a higher ratio is better for companies, investors and creditors. It means the firm would have to dispose of all current assets before it can pay off its current liabilities.
- In more detail, the working capital ratio formula compares your company assets to your current liabilities, providing a simple measure of how much you have compared to how much you owe.
- This would be worth more investigation because it is likely that the accounts payable will have to be paid before the entire balance of the notes-payable account.
- Advisory services provided by Carbon Collective Investment LLC (“Carbon Collective”), an SEC-registered investment adviser.
- This ratio was designed to assist decision-makers when determining a firm’s ability to pay its current liabilities from its current assets.
- It shows a company’s ability to pay short-term liabilities without bringing in additional cash.
In this scenario, the company would have a current ratio of 1.5, calculated by dividing its current assets ($150,000) by its current liabilities ($100,000). The cash asset ratio, or cash ratio, also is similar to the current ratio, but it only compares a company’s marketable securities and cash to its current liabilities. The acid-test ratio, also known as the quick ratio, compares a company’s quickly liquidated assets (cash, accounts receivable, and short-term investments) to its current liabilities (excluding inventory and prepaid costs). The cash asset ratio (also known as the cash ratio) is similar to the current ratio in that it compares a company’s marketable securities and cash to its current liabilities. Firstly, the current and quick ratios are both liquidity ratios that measure a company’s capacity to satisfy current debt commitments. We can calculate the current ratio using all current assets, also calculate the quick ratio using only quick assets or liquid assets.